Inlays and onlays are aesthetic dental restorations used for extensive decay, when the tooth structure is significantly damaged. These bonded fillings are made from materials such as porcelain, composite resin, or gold. The difference between inlays and onlays lies in their coverage: inlays fit within the cusp tips of the tooth, while onlays extend over one or more cusps for more extensive coverage.
What are inlays and onlays?
Inlays and onlays are dental restoration made by a dental technician, bonded to the tooth when the loss of tooth structure is too large for a traditional filling, but not extensive enough to require a crown. The inlay helps preserve the remaining healthy tooth structure by bonding an exact replica of the missing portion, much like fitting a small puzzle piece.
Inlays and onlays are used for:
- extensive decay,
- significant tooth fractures, and
- restoring canal-treated teeth.
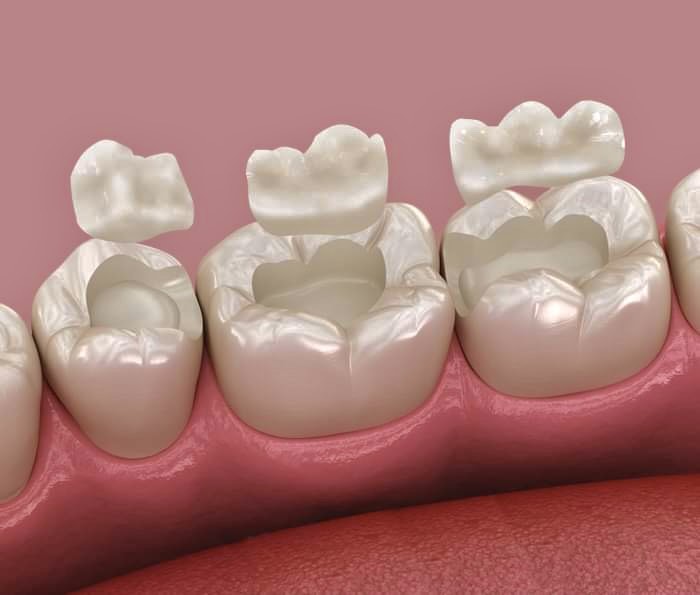
What is the difference between inlays and onlays?
An inlay covers only a portion of the tooth’s chewing surface, while an onlay extends to cover at least one of the tooth’s cusps, providing broader coverage.
Materials for dental restorations
Inlays can be made from composite resin, ceramics, or gold. Most commonly, composite inlays are used, offering high aesthetic appearance, excellent durability, and precision, while adapting to the natural tooth color.
How are inlays and onlays made?
Inlays and onlays are used for premolars and molars, particularly when decay affects multiple surfaces of the tooth or when caries have spread across several teeth. After careful surface preparation, an impression is taken and sent to a dental laboratory, where the appropriate restoration is created. While the final inlay or onlay is being made, the patient may receive a temporary filling, which will be removed before the permanent restoration is bonded.
How durable are inlays and onlays?
The durability of inlays and onlays depends on several factors. How can you ensure they last as long as possible?
- The first few hours after bonding are crucial. Avoid extremely hot or cold foods and drinks, as well as sticky or hard foods. Bite sensitivity may occur after placement and can persist for a few days.
- Maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential for longevity. Regular brushing, flossing, and interdental cleaning help remove plaque and food debris that could lead to decay around the restoration, potentially compromising its integrity.
- Limit the consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can weaken the teeth. Avoid excessive pressure on the restorations—patients with bruxism should use a night guard to protect their inlays and onlays. Stress management techniques may also help reduce grinding.
Need an inlay or onlay? Contact us by phone or book an appointment online for expert dental care. Our clinic offers state-of-the-art aesthetic dentistry services, from smile design to tartar removal.
We also have an in-house X-ray and CT lab, providing everything from small intraoral images to panoramic X-rays and 3D CT scans for precise diagnostics.



